As an Amazon affiliate, I earn from qualifying purchases at NO extra cost to you
To put on weight, your body needs to take in more calories than it burns. Eating more calories increases weight. In turn, this surplus of food increases your waistline and your body mass index (BMI). It is easier to lose weight than to gain weight. It is also important to find your lean body mass after losing weight.

Putting on weight raises your body mass Index (BMI). It also affects both your systolic blood pressure (SBP) and your diastolic blood pressure (DBP) simultaneously. You may also opt for a way to find your lean body mass to measure your body fat. Another key fact is that your blood pressure (BP) decreases significantly when you take off weight. A high BP is what you want to avoid like the plague.
Table of Contents
ToggleHigh Blood Pressure the Silent Killer
High Blood Pressure damages your arteries by making them less elastic. As a result, pressure decreases the flow of blood and oxygen to your heart and leads to heart disease. In addition, decreased blood flow to the heart causes chest pain called angina.
High Blood Pressure Symptoms
Some people experience headaches, nosebleeds, or shortness of breath with high blood pressure. However, those symptoms, oftentimes, mimic many other things (serious or non-serious). Usually, these symptoms occur once blood pressure reaches a high level over a period of time. The good news – high blood pressure is reversible with a change in diet and lifestyle.
If you don’t bring down your blood pressure, you put your life in harm’s way of developing a cardiovascular disease or something worse. High blood pressure brings with it major health challenges down the road. Journal of American Medical Association (JAMA). So, let’s try to keep your BMI at bay.
How to Figure Out Your Body Mass Index
To calculate your BMI, divide your weight in pounds by your height in inches squared, then multiply the results by a conversion factor of 703. For someone who is 5 feet 5 inches tall (65 inches) and weighs 150 pounds, the calculation would look like this: [150 ÷ (65) sq.] x 703 = 24.96.
Do you know what BMI range this is? Excellent. You are a quick learner.
Side Note:
However, scientists believe that the waist-to-hip ratio is a better measurement for healthy weight. than BMI. The ideal body fat percentage varies from person to person,
Ideal Body Fat Percentage for Women
According to the American Journal of Clinical Nutrition, there are healthy body fat percentages based on your age. For more information go to: Medical News Today 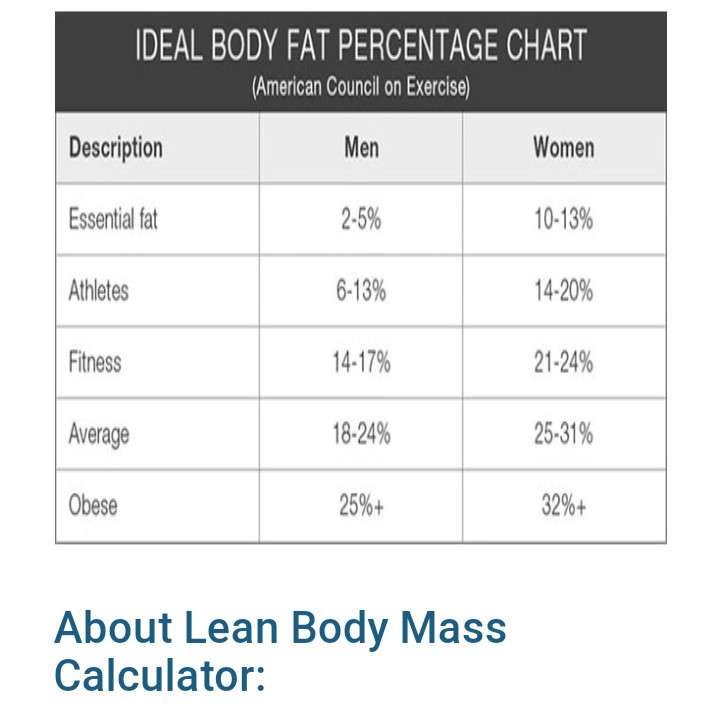
For Women:
- Ages 19 to 29 – body fat between 19 % and 22%
- Ages 30-39 – body fat between 20%and 24%
- Women in their 40s – should be between 23% and 27%
- Women 50 and older -body fat between 27% and 31% are in the healthy range (livestrong.com). Live strong, and remember to keep your BMI under control.
How to Measure Your BMI
Your BMI tells whether you have too much, too little or a just the right amount of body fat. The body mass index calculator measures body fat based on your height and weight. The formula is BMI = kg squared where kg is a person’s weight in kilograms and m sq. is their height in meters squared.
- If your BMI is less than 18.5, it falls within the underweight range.
- A BMI 18.5 to 24.9 falls within the normal or Healthy Weight range. *
- If your BMI is 25.0 to 29.9, it falls within the overweight range.
- If your BMI is 30.0 or higher, it falls within the obese range
(Red Zone)!!
Does BMI Change with Age?
BMI changes substantially with age. After about 1 year of age, BMI-for-age begins to decline, and it continues falling during the preschool years until it reaches a minimum around 4 to 6 years of age. Consequently, BMI-for-age begins a gradual increase through adolescence and most of the adulthood. BMIs for models, on the other hand, are minimal.
What BMI do Most Models Have?
As the average BMI of women has increased, the BMI for high fashion models has not. For example, a model’s BMI falls around 15 or 16. However, this is clinically underweight. Moreover, the BMIs of celebrity women are slightly higher. Most of them are in the range of 17 to 20. 
Is a BMI of 20 Skinny?
A BMI of 20-25 is typically ideal. You have no reason to worry. Ahern et al. found that a BMI of 20 is the most attractive BMI. As long as you are maintaining a healthy lifestyle, a BMI of 20 is fine. In fact, women in this range are just as capable and are just as fertile as other pregnant women. They also have successful deliveries. Here is a husband’s spin on how to figure lean body mass
for his wife’s low BMI. (Quora, 2022).
Figuring Lean Body Mass
“My wife is a skinny modelesque woman who has dimensions that fall into the middle of the model range…Do you know that this woman pushed out a 9 lbs. 2 oz baby boy. He topped the 90th percentile in terms of height and weight both in and out of the womb 2 years later.
We had no fertility issues or pregnancy issues at all with this one and one on the way. And why is this? Because:
- She is a healthy individual that takes care of herself.
- We got lucky genetically when it comes to fertility.
- BMI is a crap indicator that was created by a mathematician, not a physician 200 years ago that does not actually represent an individual’s health or size or ability to become pregnant. (Scott Richards, CEO at Rich & Rich Ventures). He is extremely happy with his wife’s Lean Body Mass.
Lean Body Mass Calculator
The Lean Body Mass Calculator computes a person’s estimated lean body mass (LBM) based on body weight, height, gender, and age. It measures your body weight, multiplies your body weight by the fat percentages, and subtracts the results from your body weight. Keep in mind, there are different calculations for women and their male counterparts. Amazon
The Lean Body Mass for Women
On average, lean body mass for women hovers around 70-75%. For men 75-85%. However, lean mass will vary up or down depending on a person’s age, hormone status, exercise volume and intensity, injury or other medical issues. Healthy women have less than 30% fat mass, and male counterparts less than 25% fat mass.
How to Determine Lean Body Mass
To determine your lean body fat mass and keep track of your fitness progress, you first need to determine your body fat percentage. Other methods to estimate or determine your LBM vary in accuracy and accessibility. Therefore, choose the option that is suitable for you.
Maintaining your lean body mass will also help keep your bones strong and keep your fat levels to a healthy minimum. This helps maintain your brain and organ functionality. With the lean body calculator, you can discover how much you would weigh without body fat. Useful if you are tracking your gains at the gym. Keeping your LBM in check helps you: 
- Keep track of your fitness goals
- Maintain your weight
- Find out how much LBM you have
- Learn how to use an LBM calculator
- Decide how much fat you should lose
Calculate Your LBM Using Height and Weight
Even though this is not a perfect measurement, you can calculate a good estimate using the height and weight formula. Enter your weight in kilograms for “W” and your height in centimeters for “H” into this equation to get your lean body mass (in kg):
- Men: Lean body mass = (0.32810 x W) +(0.33929 x H) -29.5336
- Women: Lean Body Mass = (0.29569 x W) + (0.41813 x H0 – 43.2933
- Note: 1lb = 0.453592kg, and 1 in = 2.54cm
- You can also go the easy route and use an online calculator. Amazon LBM Calculator

Simple Solutions to Lower BMI
What is Glucomannan?
Glucomannan is a natural, water-soluble dietary fiber extracted from the roots of the elephant yam, also known as konjac. It is available as a supplement, in drink mixes and is also added to food products, such as pasta and flour. It’s also the main ingredient in shirataki noodles.
Recipes
- Mushrooms, sausage, eggs, and mozzarella. Cook over warm stove. Stir in eggs and cheese and enjoy. 516 calories
2.Plain Greek Yogurt, Berries, Chopped Almonds, Tbsp. Ground, flaxseed. Stir and enjoy.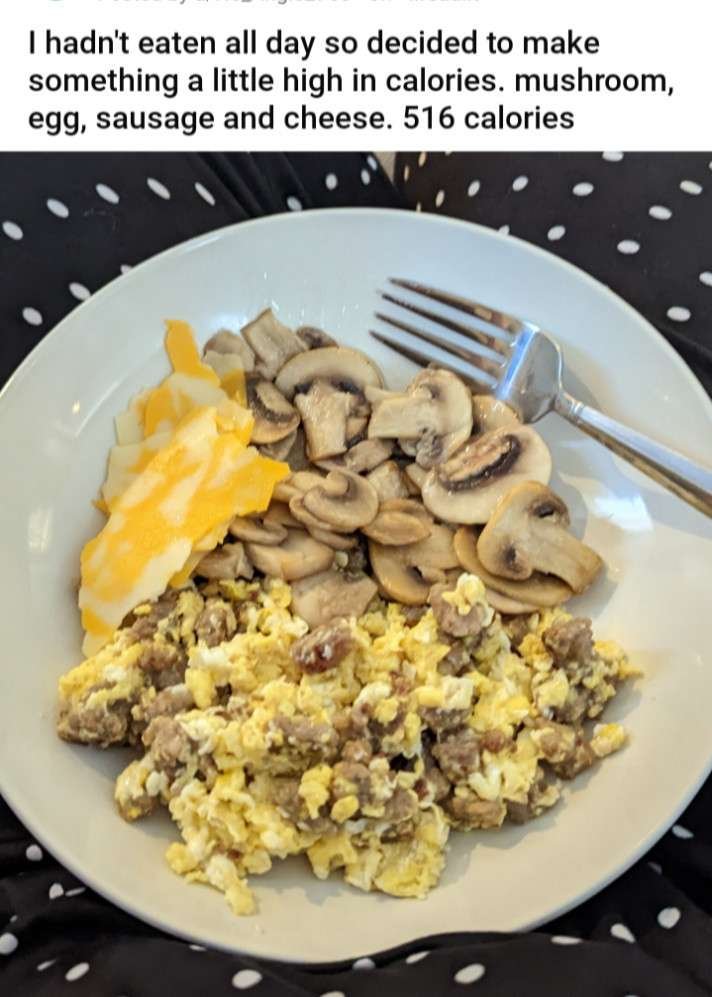 
- LYFE Kitchen
- Sweet Green
- Tender Green
- Protein Bar
- Just Salad
- Veggie Grill
- Panera Bread
- Chipotle
Americas Healthiest Chain Restaurants in Ascending order
Conclusion
Thank you for accompanying me on this wonderful BMI and Lean Body Mass journey. I hope you had as much fun as I had. It is always a good thing to keep your body, mind, and fat in check. Like Benjamin Franklin says, “an ounce of prevention is worth a pound of cure.” He was way ahead of his time.
At the end of the day, good health wins. Take your health serious. Get regular checkups and take your health to the next level. Familiarize yourself with your Body Mass Index (BMI) and with your Lean Body Mass calculator. You are worth it. Your body mass index reminds you of how much fat and lean body mass you have inside your body.
Your LBM is how much you weigh if you subtract your body fat percentage from your total weight. Sounds awesome, right? This is easier when you make use of modern technology.
Feel free to leave your questions, comments and feedback in the space provided below. I will reach out to you ASAP. In the meantime, take care of yourself, live a healthy lifestyle, and keep moving forward.
Rachele, Founder
mybluegenes.com (w)

