Latest Weight Loss Methods – The Similarities Of Wegovy And Ozempic
Over the decades, weight loss trends have evolved from crash diets and fad programs promising quick fixes to a more holistic and sustainable approach. Fast forward today and now we have some of the latest weight loss methods. 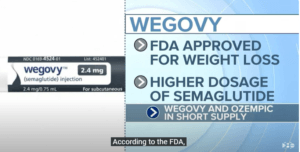
Latest Weight Loss Methods
Back in the day certain foods were considered effective for weight loss such as the grapefruit diet or the cabbage soup diet. However, these were not popular because they lacked scientific backing and often led to nutrient deficiencies. So, the latest weight loss methods, ironically, are injectable medications.
Balanced Diets and Regular Exercise
As our understanding of human physiology and nutrition advanced, the focus shifted to balanced diets and regular exercise. The rise of low-fat and low-carb diets in the 90s and 2000s brought attention to macronutrient distribution, but they were often too restrictive for long-term adherence.
Today, the emphasis is on a lifestyle change that incorporates mindful eating, portion control, and physical activity tailored to individual needs and preferences. 
Incorporating Technology into Weight Loss
Apps and Gadgets
The digital age has revolutionized weight loss efforts by providing a wealth of tools and resources at our fingertips. Smartphone applications like MyFitnessPal, LoseIt, and Noom have made it easier to track calorie intake, log physical  activity, and monitor progress.
activity, and monitor progress.
Wearable Devices
Wearable devices like Fitbit and Apple Watch have become popular for tracking steps, heart rate, and exercise intensity, allowing users to set personalized goals and monitor their progress. The rise of telehealth and virtual coaching has also made it easier to access personalized weight loss plans and expert guidance from certified nutritionists and fitness trainers, without the need for in-person appointments.
Revolutionary Dietary Approaches
Beyond Traditional Diets
While calorie counting and portion control remain essential, new dietary approaches have emerged that challenge traditional weight loss methods. Personalized nutrition based on genetic testing and metabolic markers aims to tailor dietary recommendations to an individual’s unique biology, potentially improving adherence and results.
Intermittent Fasting
Intermittent fasting and time-restricted eating patterns, such as the 16:8 method or the 5:2 diet, have gained popularity for their potential benefits in weight loss, metabolic health, and longevity. Plant-based diets, including vegetarian and vegan diets, have also gained traction as a sustainable and potentially effective approach to weight loss, with added benefits for overall health and environmental impact. 
The Psychology of Weight Loss
Behavioral Changes and Support Systems
Weight loss is not just a physical journey but also a mental and emotional one. Cognitive-behavioral strategies, such as mindful eating, stress management, and identifying and addressing emotional triggers, have become integral to successful weight loss and maintenance.
Support Groups
Support groups and communities, whether in-person or online, provide a valuable network of encouragement, accountability, and shared experiences, which significantly increase the likelihood of long-term success.
Addressing Underlying Factors
Additionally, addressing underlying psychological factors like body image issues, disordered eating patterns, and emotional eating is crucial for achieving sustainable weight loss.
Safety and Efficacy
Evaluating the Latest Weight Loss Methods
As new weight loss supplements, drugs, and programs continue to emerge, it’s essential to navigate their risks and benefits carefully. While some supplements like green tea extract or probiotics may offer modest benefits when combined with a healthy lifestyle, others may pose potential health risks or lack scientific evidence.
The same scrutiny applies to trendy weight loss programs, which often make bold claims but lack long-term safety data or sustainability. Consulting with healthcare professionals, such as registered dietitians and physicians, helps individuals evaluate the safety and efficacy of new weight loss methods and adopt evidence-based practices tailored to their unique needs and goals.
Ozempic
Ozempic (semaglutide) is a prescription medication originally developed for the treatment of type 2 diabetes. It belongs to a class of drugs called glucagon-like peptide-1 (GLP-1) receptor agonists. Ozempic works by mimicking the effects of the GLP-1 hormone, which regulates blood sugar levels and appetite. 
Pros:
1. Effective blood sugar control:
Ozempic helps lower blood sugar levels in patients with type 2 diabetes by stimulating insulin production and reducing glucose production in the liver.
2. Weight loss:
Ozempic has been shown to promote significant weight loss in patients with obesity or overweight, even in those without diabetes.
3. Cardiovascular benefits:
Studies suggest that Ozempic may reduce the risk of cardiovascular events, such as heart attacks and strokes, in patients with type 2 diabetes and established cardiovascular disease.
4. Once-weekly dosing: Ozempic is administered as a once-weekly injection, which may be more convenient for patients compared to daily medications. 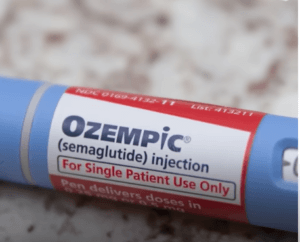
Cons:
1. Gastrointestinal side effects:
The most common side effects of Ozempic include nausea, vomiting, diarrhea, and abdominal pain.
2. Injection site reactions:
Some patients may experience redness, itching, or swelling at the injection site.
3. Risk of hypoglycemia:
When used with other diabetes medications, particularly insulin or sulfonylureas, Ozempic may increase the risk of low blood sugar (hypoglycemia).
4. Contraindications:
Ozempic should not be used in patients with a personal or family history of medullary thyroid carcinoma or multiple endocrine neoplasia syndrome type 2, as it may increase the risk of thyroid tumors in these individuals.
Weight Loss Effects
Ozempic has been found to promote significant weight loss in patients with obesity or overweight, even in those without diabetes. In clinical trials, patients using Ozempic lost an average of 15% of their body weight over 68 weeks when combined with lifestyle modifications. The medication reduces appetite, slows gastric emptying, and increases feelings of fullness, leading to reduced calorie intake and weight loss. 
New Research and Prevalence
Due to its effectiveness in promoting weight loss, the off-label use of Ozempic for obesity treatment has become increasingly prevalent. In 2021, the FDA approved a higher-dose formulation of semaglutide called Wegovy specifically for chronic weight management in adults with obesity or overweight with at least one weight-related comorbidity.
Ozempic for Other Conditions
Recent studies have also investigated the potential of Ozempic in treating other conditions, such as non-alcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD) and polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS), which are often associated with obesity and insulin resistance.
The growing popularity of Ozempic and similar GLP-1 receptor agonists for weight loss has led to increased demand, In some cases, shortages of the medication. This has raised concerns about ensuring an adequate supply for patients who require the drug for its original indication of type 2 diabetes management.
Although Ozempic and Wegovy have different names, they are both synthetic forms called semaglutide and are used for weight loss. 
Wegovy
Wegovy® (semaglutide) is an injectable prescription medication used along with diet and exercise for two purposes:
1. To reduce the risk of major cardiovascular events like death, heart attack, or stroke in adults with existing heart disease who are obese or overweight.
2. To help adults and children aged 12+ who have obesity, or some overweight adults with weight-related medical issues, lose excess weight and keep it off. 
Some Important Safety Information
Wegovy® may increase the risk of thyroid tumors, including cancer. It should not be used by those with a personal/family history of a thyroid cancer called medullary thyroid carcinoma or the condition Multiple Endocrine Neoplasia syndrome type 2.
It causes inflammation of the pancreas, gallbladder problems, low blood sugar, kidney issues, allergic reactions, vision changes in type 2 diabetes patients, increased heart rate, and mental health side effects like depression/suicidal thoughts.
Common side effects include nausea, diarrhea, vomiting, constipation, abdominal pain, headache, fatigue, and others.
Patients should discuss their full medical history and medications with their healthcare provider before starting Wegovy®. 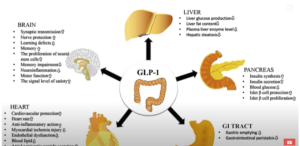
Disclaimer:
Due to the prevalency of obesity and over weight people across the nation and across the globe, we need a solution to this epidemic like yesterday. Carrying excessive weight leads to a litany of health conditions.
The latest weight loss methods are apparently saving lives on a grand scale. However, please consult with your doctor first before starting any type of weight loss program.
Founder, Rachele
(website) mybluegenes.com
(email) rachele@ mybluegenes.com