Underactive Thyroid In Women – Major Impact On The Body
Natural Ways to Balance Your Hormones – Discover 8 Organic ApproachesHypothyroidism, also known as an underactive thyroid in women, is a condition in which the thyroid gland fails to produce sufficient amounts of thyroid hormones.
These hormones, particularly thyroxine (T4) and triiodothyronine (T3), play a crucial role in regulating various bodily functions, including metabolism, heart rate, body temperature, and energy levels. Underactive Thyroid in women is more common than you think.
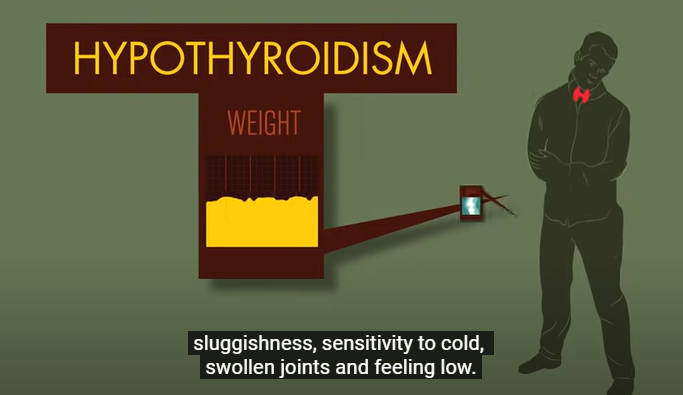
When the thyroid gland is underactive, it leads to a wide range of symptoms and health issues, such as fatigue, weight gain, cold sensitivity, dry skin, hair loss, constipation, and depression. If left untreated, hypothyroidism has a significant impact on an individual’s overall well-being and quality of life.
Women are More Prone to Thyroid Issues
Women are significantly more likely to develop thyroid disorders, including hypothyroidism, compared to men. In fact, it is estimated that women are five to eight times more susceptible to thyroid problems than their male counterparts.
This gender disparity is attributed to several factors such as :
- Hormonal changes
- Autoimmune conditions
- Genetic predisposition.
Women’s bodies undergo numerous hormonal fluctuations throughout their lives, particularly during puberty, pregnancy, and menopause.
Hormonal Imbalances
These hormonal shifts sometimes trigger the development of thyroid issues. Additionally, autoimmune disorders, such as Hashimoto’s thyroiditis, a leading cause of hypothyroidism, are more common in women.
Genetic Predisposition
Genetic factors also play a role. If there is a family history of thyroid disorders it increases the risk of developing hypothyroidism. One way to hone in on your genetics is by doing a DNA test. You’ll be surprised by what you find. Also, ask your primary healthcare professional about administering genogram.
Hypothyroidism in Women
Women with an underactive thyroid experience a wide array of symptoms. These vary in severity from person to person.
Some of the most common symptoms include:
1. Fatigue and weakness
2. Unexplained weight gain or difficulty losing weight
3. Sensitivity to cold temperatures
4. Dry skin and hair
5. Hair loss or thinning
6. Constipation
7. Muscle aches and joint pain
8. Depression or mood changes
9. Memory problems or difficulty concentrating
10. Irregular menstrual cycles or heavy menstrual bleeding
It is important to note that these symptoms are subtle and develop gradually over time. Therefore, it is a challenge to recognize the presence of an underactive thyroid.
The importance of thyroid hormones in women’s health:
 Thyroid hormones play a vital role in maintaining overall health and well-being, particularly in women. These hormones are essential for regulating metabolism. They affect your energy levels, weight management, and the functioning of various organs.
Thyroid hormones play a vital role in maintaining overall health and well-being, particularly in women. These hormones are essential for regulating metabolism. They affect your energy levels, weight management, and the functioning of various organs.
Thyroid Hormones and Reproductive Health
In women, thyroid hormones also have a significant impact on reproductive health. Adequate levels of thyroid hormones are necessary for proper ovarian function, menstrual regularity, and fertility. Hypothyroidism can lead to menstrual irregularities, such as heavy or prolonged periods, and can even contribute to infertility.
During pregnancy, thyroid hormones are crucial for fetal development, especially in the early stages when the fetal thyroid gland is not yet functional. Maternal hypothyroidism can increase the risk of complications, such as miscarriage, preterm birth, and neurodevelopmental issues in the child. Therefore, it is essential for women to maintain optimal thyroid function throughout their lives to promote overall health and well-being.
Recognizing the Symptoms
Identifying Early Signs of Underactive Thyroid
Hypothyroidism, or an underactive thyroid, is a pretty sneaky condition. It gradually affects various aspects of your health. Recognizing the early signs is crucial for timely intervention and management. 
Common Indicators of an Underactive Thyroid
Common indicators include unexplained fatigue, weight gain despite no changes in diet or exercise, cold sensitivity, dry skin, hair loss, constipation, and muscle aches. If you experience these symptoms persistently, it’s important to consult your healthcare provider.
The Critical Nature of Early Detection
Early detection is key to preventing complications and managing hypothyroidism effectively. Untreated hypothyroidism leads to higher cholesterol levels, increased risk of heart disease, and in severe cases, myxedema coma. This is a life-threatening condition.
Regular thyroid function tests, especially if you have a family history of thyroid disorders or autoimmune conditions, helps catch any abnormalities early on.
Navigating Hypothyroidism
For women, hypothyroidism significantly impacts menstrual cycles and fertility. Irregular periods, heavy menstrual bleeding, or even absence of menstruation (amenorrhea) are clear red flags.
Irregular Menstrual Cycle and Fertility
Thyroid hormones play a crucial role in regulating the menstrual cycle, and imbalances disrupt ovulation and affect fertility. If you’re struggling with menstrual irregularities or having difficulty conceiving, it’s worth getting your thyroid function evaluated.
When Fatigue and Weight Changes
Fatigue is a common complaint. Consequently, when it’s persistent and accompanied by unexplained weight changes, it warrants a closer look at your thyroid health. Hypothyroidism slows down your metabolism. This, in turn leads to weight gain despite maintaining a healthy diet and exercise routine. 
Hyperthyroidism and Weight Loss
On the flip side, sudden weight loss without any lifestyle changes could indicate an overactive thyroid (hyperthyroidism). If you’re experiencing significant fatigue or weight fluctuations, don’t hesitate to discuss these concerns with your doctor.
Early Diagnosis and Treatment
Remember, your thyroid gland is a small but mighty organ that influences various systems in your body. Paying attention to subtle changes and seeking help when needed makes a big difference in your overall well-being.
Early diagnosis and appropriate treatment helps you manage hypothyroidism effectively and maintain optimal health. Whether you are experiencing an over or underactive thyroid, consulting with you primary care expert is key.
Diagnosis and Testing
When it comes to thyroid disorders, accurate diagnosis and testing are crucial for developing a personalized treatment plan. Healthcare providers play a vital role in this process. By utilizing various tools and techniques to assess thyroid function thyroid specialists determine the best course of action for each individual patient.
Blood Tests for Thyroid Function
Blood tests are the primary means of evaluating thyroid function. The most common tests include measuring levels of Thyroid Stimulating Hormone (TSH), Free Thyroxine (FT4), and Free Triiodothyronine (FT3).
Thyroid-Stimulating Hormone (TSH)
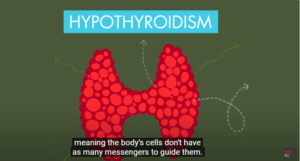
Thyroid-Stimulating Hormone (TSH) is produced by the pituitary gland. It stimulates the thyroid to produce hormones. High TSH levels indicate an underactive thyroid (hypothyroidism). Needless to say, low levels suggest an overactive thyroid (hyperthyroidism).
FT4 and FT3 tests measure the amount of available thyroid hormones in the blood. Abnormal levels of these hormones provide further insight into the specific nature of the thyroid disorder.
The Role of Healthcare Providers
Review Medical Records
Healthcare providers, such as endocrinologists and primary care physicians, are essential in diagnosing thyroid issues. They begin by reviewing the patient’s medical history, symptoms, and physical examination findings.
Blood Tests, Ultrsounds, and X-Rays
If a thyroid disorder is suspected, they will order appropriate blood tests and interpret the results. In some cases, imaging tests like ultrasounds or radioactive iodine uptake scans are necessary to visualize the thyroid gland and assess its function.
Healthcare providers also consider other factors when making a diagnosis and developing a treatment plan.
For example, they take into consideration:
- The patient’s age
- Family history
- Co-existing medical conditions
Thyroid-Stimulating Hormones
Thyroid-Stimulating Hormones (TSH) levels are a key indicator of thyroid function. They play a significant role in guiding treatment decisions. The normal range for TSH is typically between 0.4 and 4.0 mIU/L.
Underactive Thyroid Range
However, this range varies slightly depending on the laboratory. If TSH levels are above the normal range, it suggests an underactive thyroid. In this case, thyroid hormone replacement therapy is a viable option.
Overactive Thyroid Range
Conversely, if TSH levels are below the normal range, it indicates an overactive thyroid. In this case treatment options will include antithyroid medications, radioactive iodine therapy, or surgery. Regular monitoring of TSH levels is essential to ensure that treatment is effective and to make adjustments as needed.
Treatment Options
The treatment for hyperthyroidism in women depends on the underlying cause, severity of the condition, age, and overall health.
The main treatment options include:
- Anti-thyroid medications: Drugs like methimazole and propylthiouracil (PTU) can block the production of thyroid hormones and are often the first line of treatment.
- Radioactive iodine therapy: This treatment involves taking a single dose of radioactive iodine orally, which is absorbed by the thyroid gland and destroys the overactive thyroid cells.
- Surgery (Thyroidectomy): In some cases, surgical removal of part or all of the thyroid gland may be recommended, especially if there is a large goiter or if the patient cannot tolerate other treatments.
- 4. Beta-blockers: These medications do not treat the underlying cause but can help alleviate symptoms such as rapid heart rate, tremors, and anxiety until other treatments take effect.
- Treating the underlying cause: If hyperthyroidism is caused by a specific condition, such as Graves’ disease or a thyroid nodule, treating that condition helps resolve hyperthyroidism.
After treatment, patients may develop hypothyroidism and require lifelong thyroid hormone replacement therapy. Regular monitoring of thyroid function and adjusting the treatment as needed is crucial. The choice of treatment depends on individual factors, and it is essential to consult with an endocrinologist to determine the best approach for each patient.
Family Friend With Hyperthyroidism
In retrospect, I still remember my mom’s friend. She had this overactive thyroid gland on one side of her neck. I was never sure why she never had her goiter removed. It must of effected how she swallowed food. However, she never complained, at least when she came to visit.
Considering the size of her thyroid, one would expect her to be a little cranky. However, she was always pleasant. She was a perfect candidate for a thyroidectomy. At least from my point of view.
The Psychological Impact of a Diagnosis
The process of waiting for a thyroid disorder diagnosis is emotionally challenging for patients. Symptoms such as fatigue, weight changes, and mood disturbances will significantly impact daily life. These symptoms lead to anxiety and frustration.
During this time, it is essential for healthcare providers to offer support and reassurance/ In addition your medical team will also provide clear information about the diagnostic process and expected timelines.
Patients will also benefit immensely from activities such as:
- Meditation
- Relaxation
- Deep Breathing
- Stress-management techniques
Joining support groups or connecting with others who have experienced similar challenges also provides a sense of community and it reduces the feelings of isolation.
If the psychological impact becomes severe, patients should not hesitate to seek help from mental wellness professionals who offer additional coping strategies and support.
Treatment Strategies for Underactive Thyroid in Women
Underactive thyroid, or hypothyroidism, is a common condition affecting many women worldwide. Fortunately, there are several effective treatment strategies available to manage the symptoms and restore optimal thyroid function. Let’s explore some of these options and how they help women lead healthier lives.
Levothyroxine and Other Medication Options
The primary treatment for underactive thyroid is thyroid hormone replacement therapy. It is typically in the form of levothyroxine. This synthetic hormone mimics the effects of the naturally produced thyroid hormone, thyroxine (T4).
Levothyroxine
Levothyroxine is taken orally, usually once daily, and works to restore normal thyroid hormone levels in the body. Dosage is carefully adjusted based on individual needs and regular blood tests.
Liothyronine (T3)
In some cases, other thyroid hormone preparations, such as liothyronine (T3) or natural desiccated thyroid (NDT), are prescribed alone or in combination with levothyroxine. Of course, this depends on the patient’s response and specific requirements.
Lifestyle Adjustments
In addition to medication, making certain lifestyle changes significantly impact thyroid health and overall well-being. Adopting a balanced, nutrient-rich diet helps support a thyroid condition.
Here are a few suggestions to include in your diet:
- Iodine
- Selenium
- Zinc
Regular exercise, such as low-impact activities like walking, swimming, or yoga, helps boost energy levels, improve mood, and maintain a healthy weight. Managing stress through relaxation techniques, mindfulness, or therapy is also beneficial. Oftentimes chronic stress will interfere with thyroid hormone production.
Avoid Cruciferous Vegetables
Additionally, avoiding excessive consumption of goitrogens, substances found in certain foods like raw cruciferous vegetables, will help optimize thyroid function. 
Here are a list of these types of vegetables to avoid:
- Cauliflower
- Cabbage
- Kale
- Broccoli
Navigating Treatment During Pregnancy and Postpartum
Proper management of underactive thyroid is crucial during pregnancy and the postpartum period. Thyroid hormones play a vital role in fetal development, particularly in the first trimester. Inadequate thyroid hormone levels increase the risk of complications such as miscarriage, preterm delivery, and impaired cognitive development in the child.
Pregnant women with hypothyroidism typically require an increase in their levothyroxine dosage to meet the increased demand for thyroid hormones. Close monitoring through regular thyroid function tests are highly recommended. Your physician will make adjustments to medication dosage as they see fit.
Your healthcare guidance is quintessential throughout pregnancy and the postpartum period. This ensures the health of both mother and baby.
Monitoring and Adjusting Treatment Over Time
Effective treatment of underactive thyroid requires ongoing monitoring and adjustment. Thyroid function tests, including TSH (thyroid-stimulating hormone) and free T4 levels, must be regularly assessed to ensure that the medication dosage remains appropriate.
Over time, the dosage will be modified based on changes in your weight, age, other health conditions, or the development of new symptoms.
Women are required to work closely with their healthcare provider. This helps to track their progress, discuss any concerns, and make necessary adjustments to their treatment plan. With proper management and regular follow-up, most women with underactive thyroid will expect a favorable outcome.
They will be able to do such things as:
- Achieve symptom relief
- Improved quality of life
- Long-term well-being.
Support and Management
Living with hypothyroidism no doubt is challenging. However, with the right support and management strategies, you will lead a healthy and fulfilling life. It’s essential to work closely with your healthcare provider to develop a comprehensive treatment plan that addresses your specific needs.
Monitor Hormone Levels
This includes regular monitoring of your thyroid hormone levels, adjusting your medication dosage as needed, and making lifestyle changes to support your overall health and well-being.
The Importance of Patient Advocacy
Informed Health Decisions
As a patient with hypothyroidism, it’s crucial to be an active participant in your healthcare decisions. Educate yourself about your condition, ask questions, and don’t hesitate to advocate for yourself if you feel your concerns are not being addressed.
Stay informed about the latest research and treatment options and discuss any changes or new approaches with your healthcare provider. Remember, you are the expert on your own body and experiences, and your input is valuable in shaping your treatment plan.
Support Groups and Online Resources for Women
Connecting with others who share similar experiences is incredibly helpful when living with hypothyroidism. Many women find support groups, both in-person and online. There are lots of invaluable information, lots of encouragement, and a plethora of resources.
Blogs & Forums
These communities provide a safe space to share your struggles, celebrate your successes, and learn from others who have faced similar challenges. Additionally, there are numerous online resources, such as blogs, forums, and websites dedicated to hypothyroidism, They offer a wealth of information and support.
Long-Term Health Monitoring and Prevention
Hypothyroidism increase your risk of developing other health conditions, such as heart disease, osteoporosis, and depression. That’s why it’s essential to maintain regular check-ups with your healthcare provider and stay proactive about your long-term health.
Your doctor will recommend periodic screening tests to monitor your bone density, cholesterol levels, and mental fitness. By dealing with any potential issues early on, you take steps to prevent or manage related conditions and maintain optimal health.
Creating a Sustainable Lifestyle
Living well with hypothyroidism often involves making lifestyle changes that support your overall health and help manage your symptoms. This includes adopting a balanced, nutrient-rich diet that includes plenty of fruits, vegetables, lean proteins, whole grains and other types of fortified foods.
Adopting a Healthy Lifestyle
Regular exercise, stress management techniques, and getting enough quality sleep are also important for maintaining energy levels and promoting overall well-being. It’s essential to find a sustainable routine that works for you and your unique needs, rather than trying to adhere to a one-size-fits-all approach.
Be patient with yourself, celebrate small victories, and don’t hesitate to reach out for support when you need it.
Founder, Rachele
(w) mybluegenes.com
rachele@ mybluegenes.com